1.4 Expressiveness of Encodings
Topic Summary
In Topic 4 of Lesson 1 we will consider the first of two criteria we can use to evaluate an encoding: expressiveness. Expressiveness means that the chosen encoding expresses all of, and only, what’s in the data. To better understand the concept of expressiveness, we’ll consider at examples in which an encoding can fail the expressiveness criteria, such as: 1) by showing ordered data in a way that doesn’t express any order at all, 2) by showing ordered data in a way that expresses the wrong order and 3) by showing unordered data in a way that expresses some order. Expressiveness relates to more than just order, and we’ll consider more scenarios as we go along.
Key Points to Remember
- According to Tamara Munzner, “the expressiveness principle dictates that the visual encoding should express all of, and only, the information in the dataset attributes.”
- We must look at ways in which encoding might fail to express all of, and only, the information in the dataset attributes. Three ways of many in which a data visual can fail the expressiveness criteria are as follows:
- By showing ordered data in a way that doesn’t express any order at all.
- By showing ordered data in a way that expresses the wrong order.
- By showing unordered data in a way that expresses some order.
Diagrams
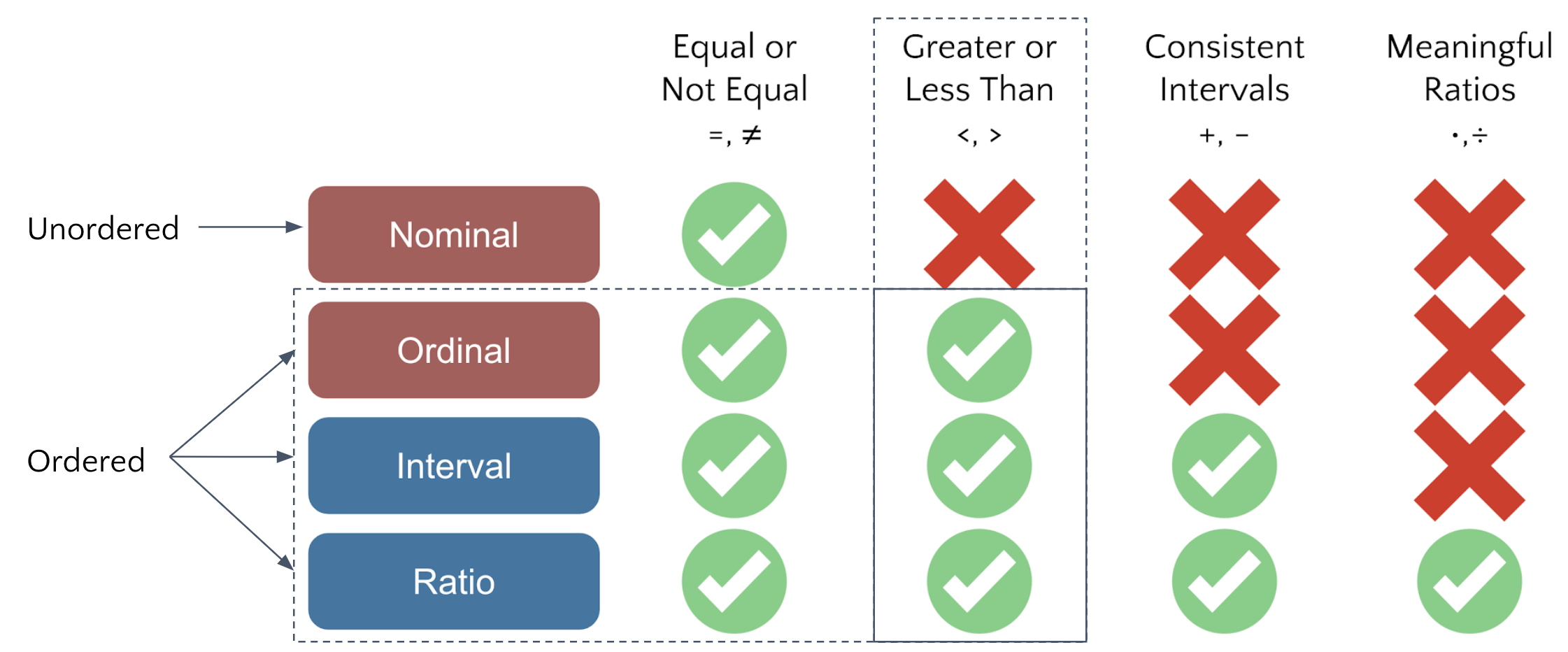
Only ordinal, interval and ratio scales are ordered
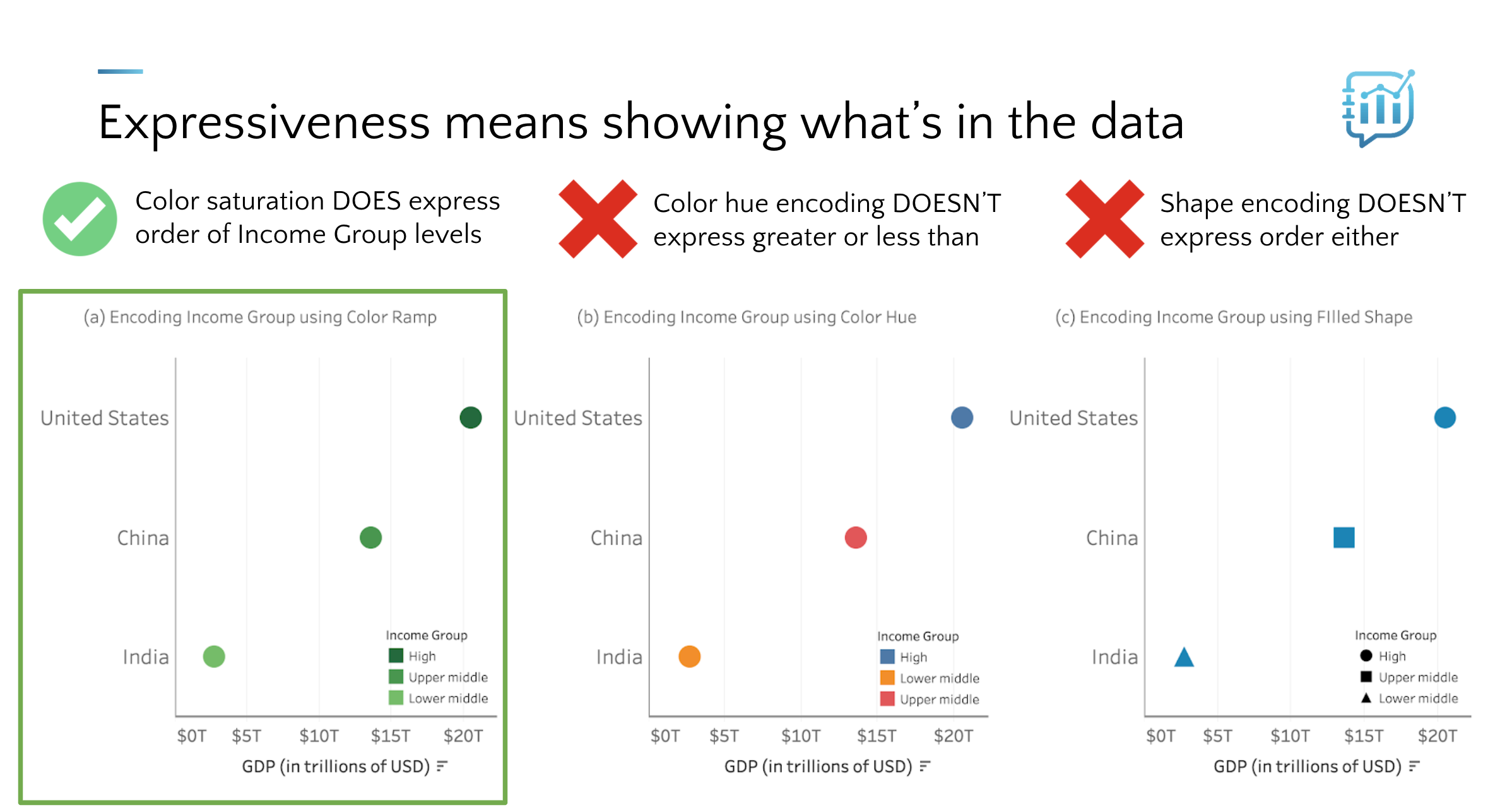
Comparing an encoding type that expresses the inherent order of an ordinal variable with two that don’t
Exercises
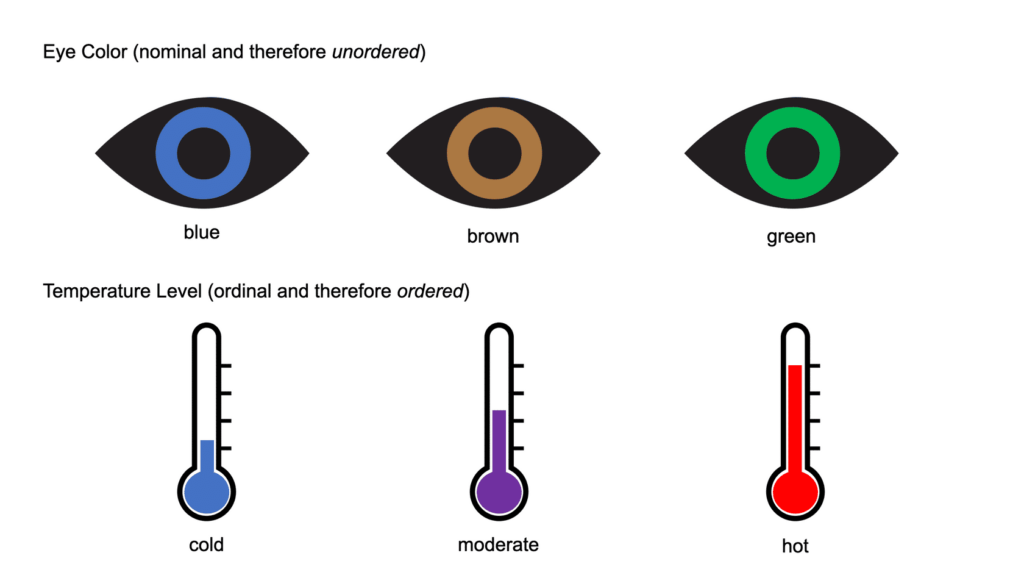
Exercise 1.4. In the Lesson 1 Exercise Worksheet or on a sheet of blank paper, sketch marks that express the three (unordered) levels of the nominal variable on the left. Then sketch different marks that express the three (ordered) levels of the ordinal variable on the right:
Eye color (blue, brown, green):
Temp level (cold, moderate, hot):
Expand for Solution to Exercise 1.4
These are examples of icons that could be used as graphical marks to encode two different variables – a nominal one and an ordinal one. Notice that the icons for eye color do not express order of any kind, while the icons for temperature level express order with the thermometer positions as well as the common blue-red color convention for cold and hot.
Quotes
“Graphic design issues are codified with expressiveness and effectiveness criteria. Expressiveness criteria identify graphical languages that express the desired information. Effectiveness criteria identify which of these graphical languages, in a given situation, is the most effective at exploiting the capabilities of the output medium and the human visual system.”
Jock Mackinlay
Further Learning
- Research paper: “Automating the Design of Graphical Presentations of Relational Information” by Jock Mackinlay